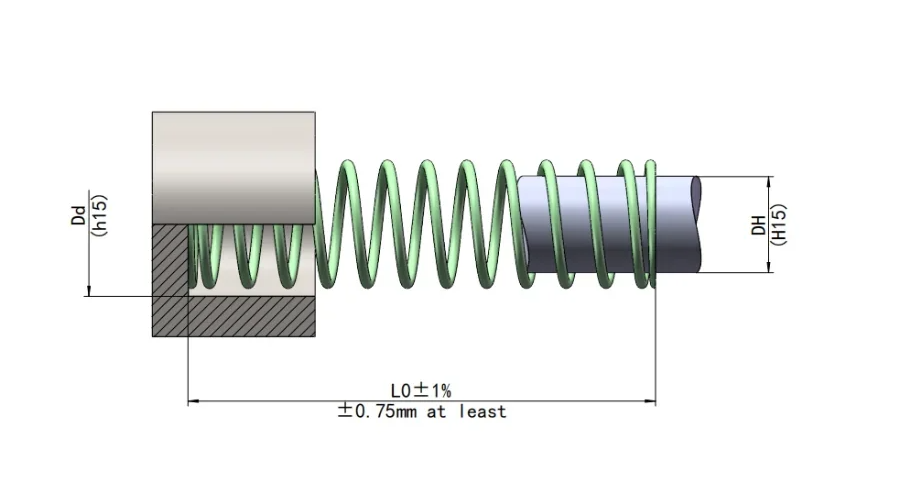
Product center
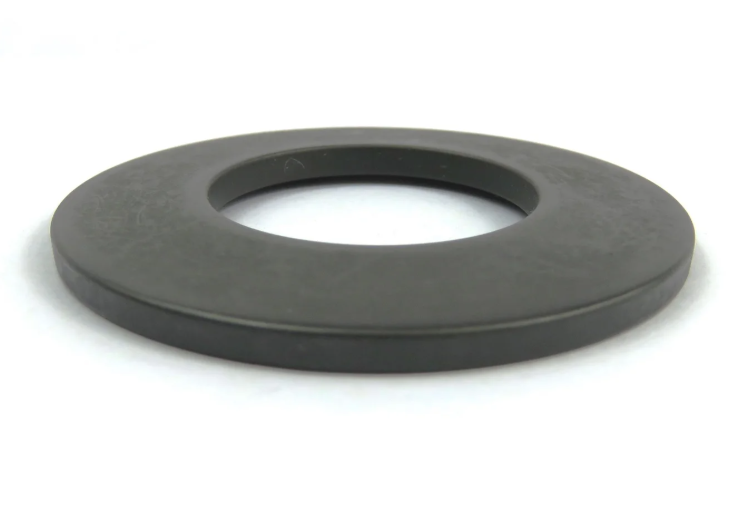
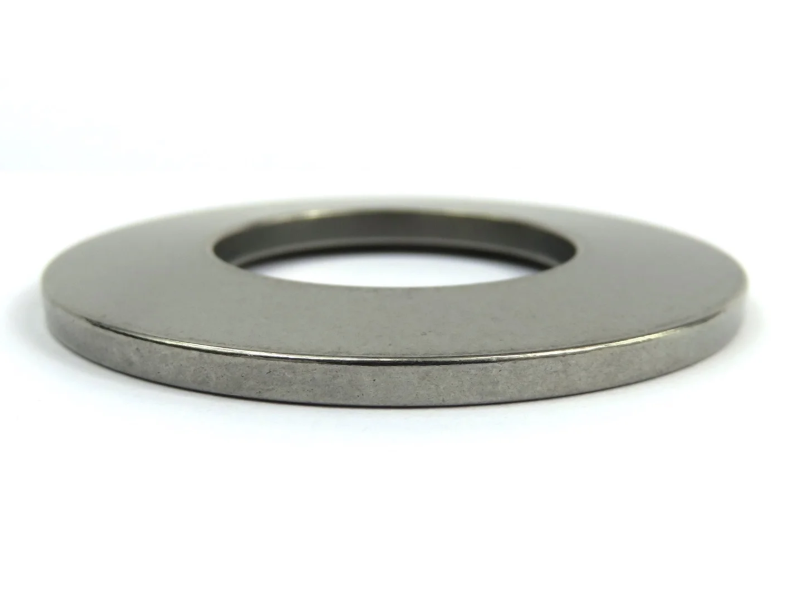
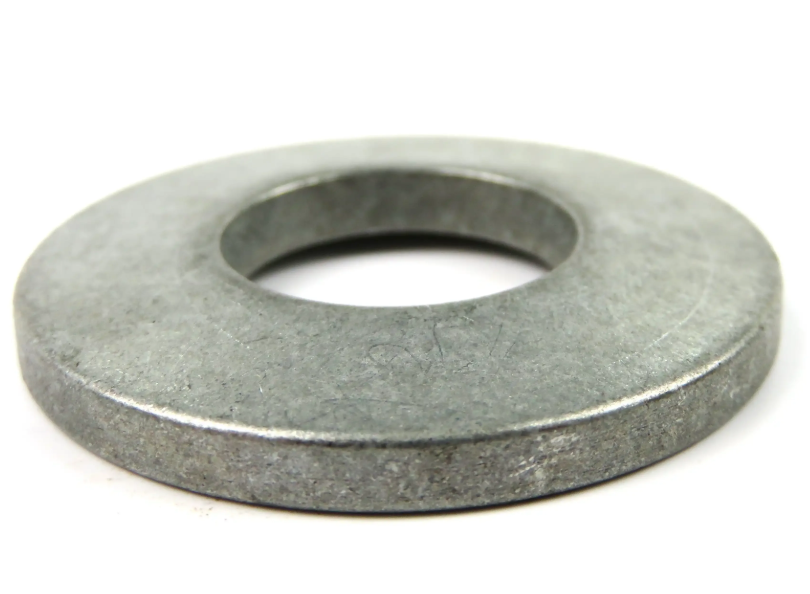
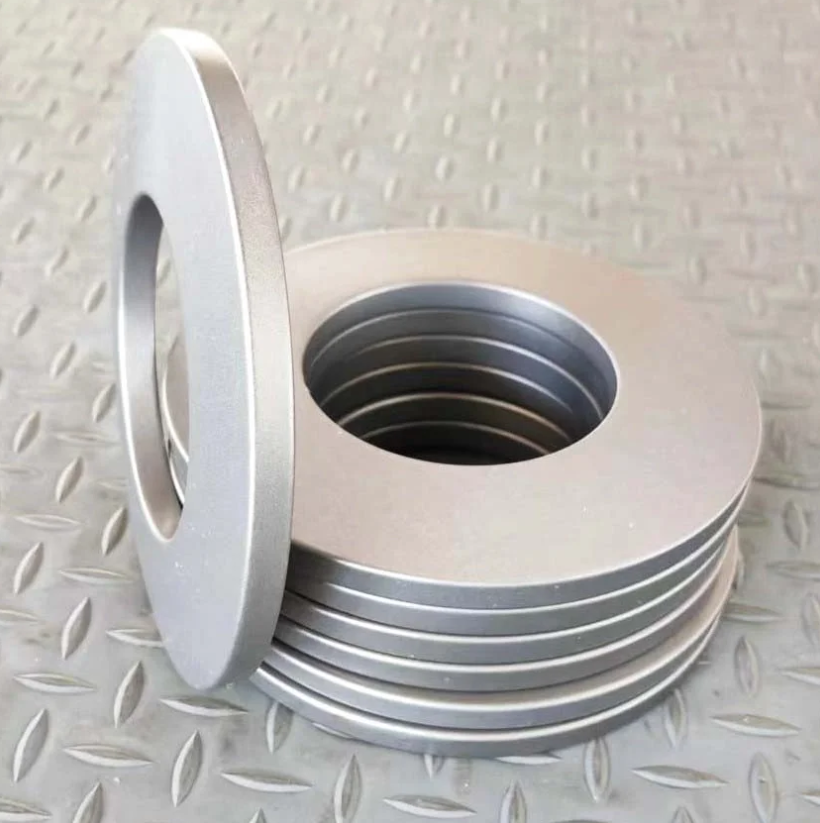
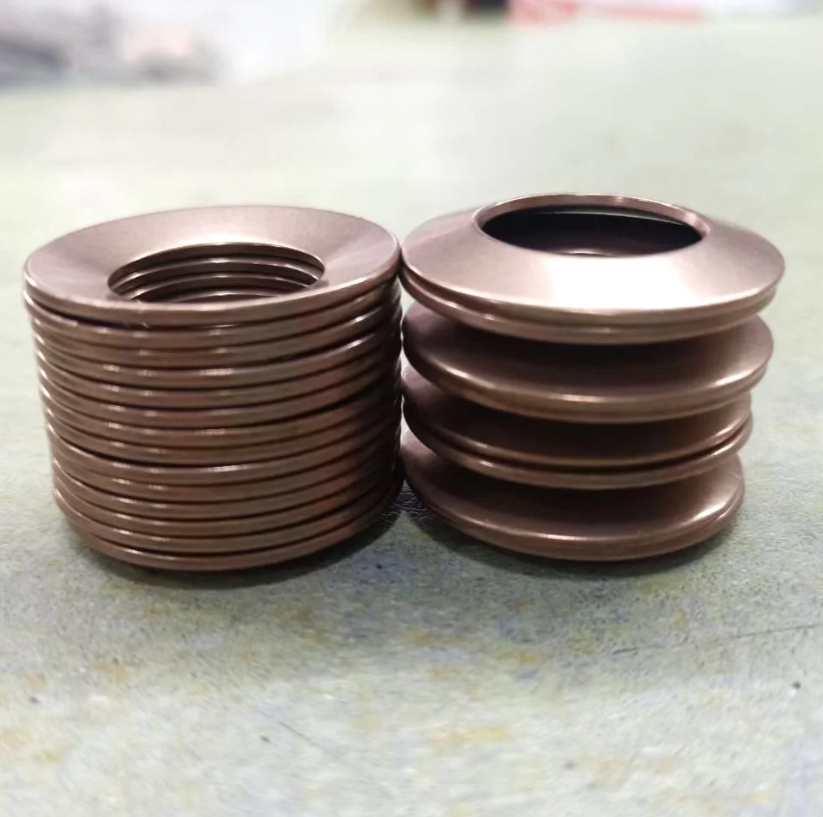
Disc Spring - Series A
PRODUCT DETAILS:
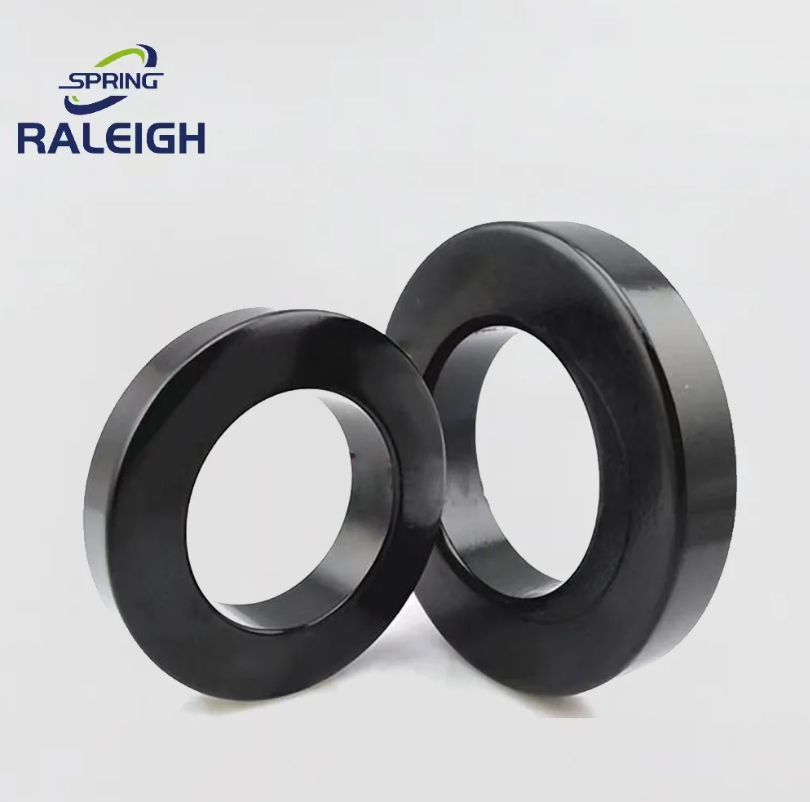
Disc springs are annular coned elements that offer resistance to a compressive load applied axially. They may be designed as single disc springs or as disc springs stacked in parallel or in series, either singly or in multiples. They may be subjected to both static and fatigue loading, and may have flat bearings.
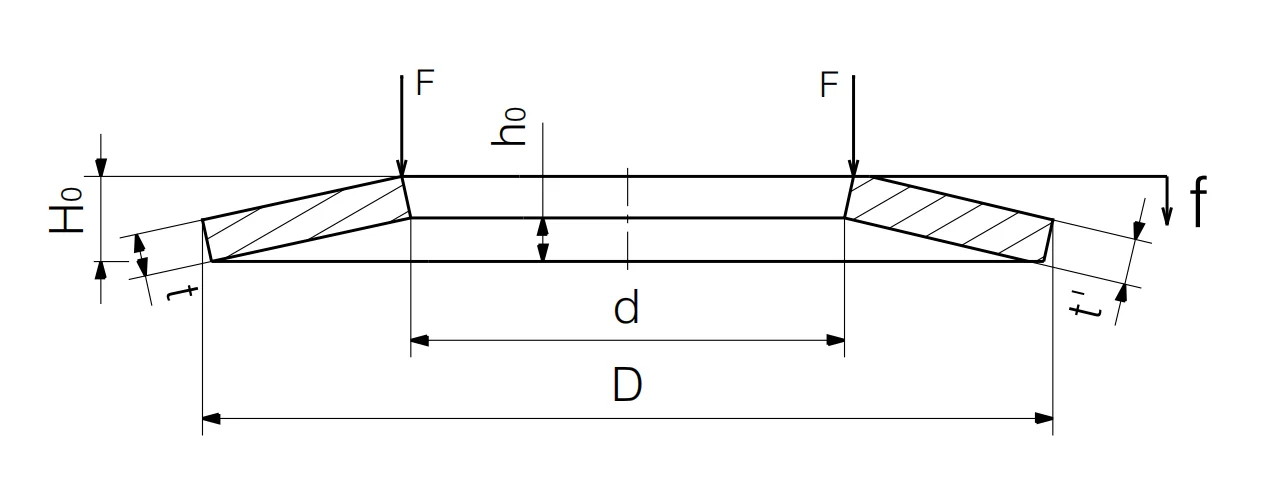
Raleigh Spring provide DIN2093 Metric Disc Washer Series to meet all kinds of applications, and also expand on size options base on DIN 2093 table, made to DIN manufacturing and quality specifications to provide component flexibility for product designers. Raleigh DIN2093 Disc Washers could be made according to your requirements.
Disc spring groups
Group | Thickness [t] | With flat bearings and reduced thickness |
Group 1 | <1.25 | No |
Group 2 | 1.25 ≤ t ≤6 | No |
Group 3 | 6 <t ≤ 14 | Yes |
Characteristics
Own high stiffness and great buffer and shock absorption capacity; be able to undertake huge loads by small deformation and is suitable for the occasions where the axial space is relatively small.
This type of spring is featured by variable stiffness and broad non-linearity.
Different combination methods of the same disc springs can lead to different spring characteristics. The combination methods combing the springs with different thicknesses and plate number can also be adopted.
Assembling
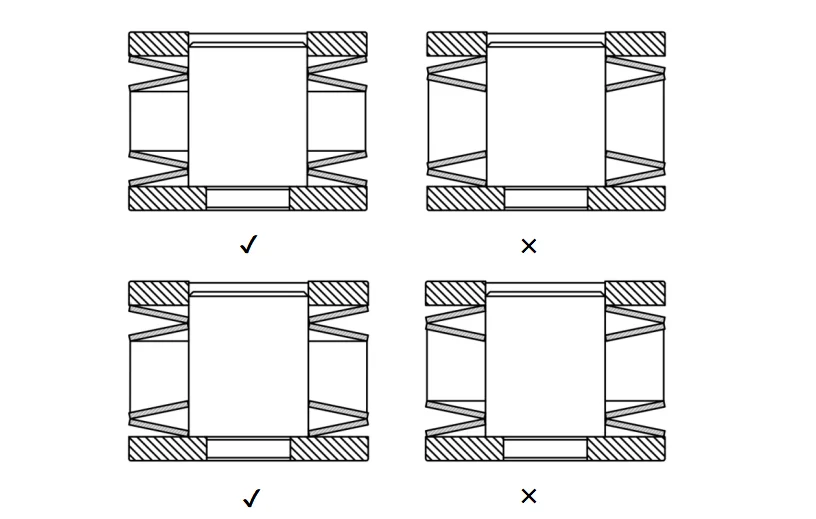
Disc orientation when assembling, is important to guarantee a correct functioning of the stack and its long life. Basically the disc which is in contact with the edge has to be held by its outer edge. This reduces contact pressure, as the same force is acting over a bigger surface. That reduces the possibility of contact areas cracking. If the number of discs used is not even, the disc which will be held by its outer edge is the one on the side where the force is occurring.
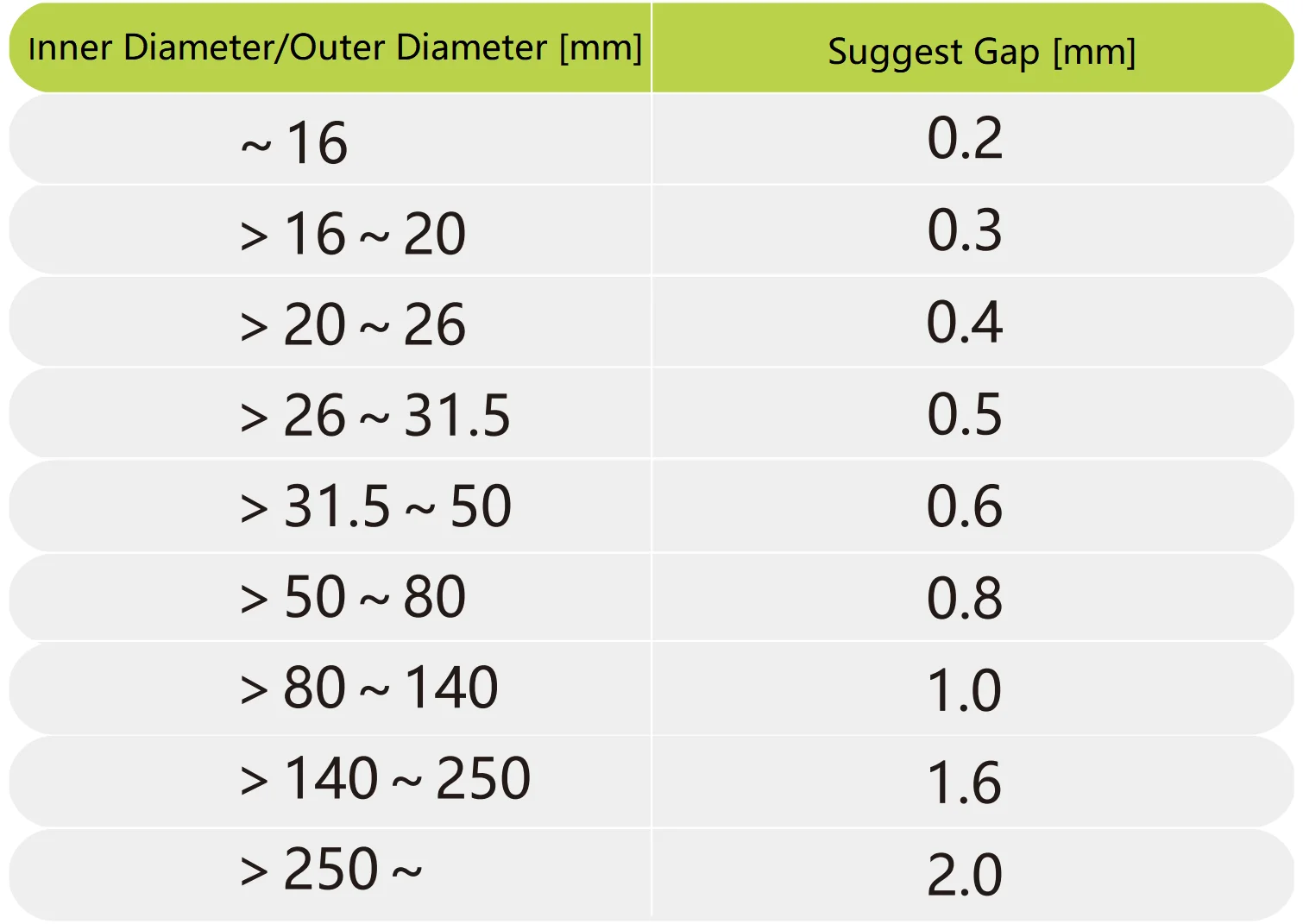
The guide bar (internally-guided) or guide bush (externally-guided) shall be adopted as the guiding part of disc spring. Here is the table of recommended size of gaps between guiding parts and disc spring.
Tolerance
- The following deviations are laid down in DIN EN 16983 (Previously DIN2093) standards:
Tolerances on thickness, free overall height & spring load
Outer Diameter/ Inner Diameter | OD | ID | ||
H12 | H13 | H12 | H13 | |
8 ~ 10 | -0.15 | -0.22 | + 0.15 | + 0.22 |
>10 ~ 18 | -0.18 | -0.27 | + 0.18 | + 0.27 |
>18 ~ 30 | -0.21 | -0.33 | + 0.21 | + 0.33 |
>30 ~ 50 | -0.25 | -0.39 | + 0.25 | + 0.39 |
>50 ~ 80 | -0.30 | -0.46 | + 0.30 | + 0.46 |
>80 ~ 120 | -0.35 | -0.54 | + 0.35 | + 0.54 |
>120 ~ 180 | -0.40 | -0.63 | + 0.40 | + 0.63 |
>180 ~ 250 | -0.46 | -0.72 | + 0.46 | + 0.72 |
>250 ~ 315 | -0.52 | -0.81 | + 0.52 | + 0.81 |
>315 ~ 400 | -0.57 | -0.89 | + 0.57 | + 0.89 |
>400 ~ 500 | -0.63 | -0.97 | + 0.63 | + 0.97 |
- Tolerances on thickness, free overall height & spring load
Group | t | t tolerance | Ho tolerance | F (0.75%) tolerance |
1 | 0.2 ≤t≤ 0.6 | +0.02/-0.06 | +0.1/-0.05 | +25%/-7.5% |
0.6<t<1.25< p="" style="box-sizing: border-box; word-break: break-word !important; overflow-wrap: break-word;"> | +0.03/-0.09 | |||
2 | 1.25≤t≤2 | +0.04/-0.12 | +0.15/-0.08 | +15%/-7.5% |
2<t≤3< p="" style="box-sizing: border-box; word-break: break-word !important; overflow-wrap: break-word;"> | +0.2/-0.1 | |||
3<t≤3.8< p="" style="box-sizing: border-box; word-break: break-word !important; overflow-wrap: break-word;"> | +0.3/-0.15 | +10%/-5% | ||
3.8<t≤6< p="" style="box-sizing: border-box; word-break: break-word !important; overflow-wrap: break-word;"> | +0.05/-0.15 | |||
3 | 6<t≤14< p="" style="box-sizing: border-box; word-break: break-word !important; overflow-wrap: break-word;"> | ±0.1 | ±0.3 | ±5% |
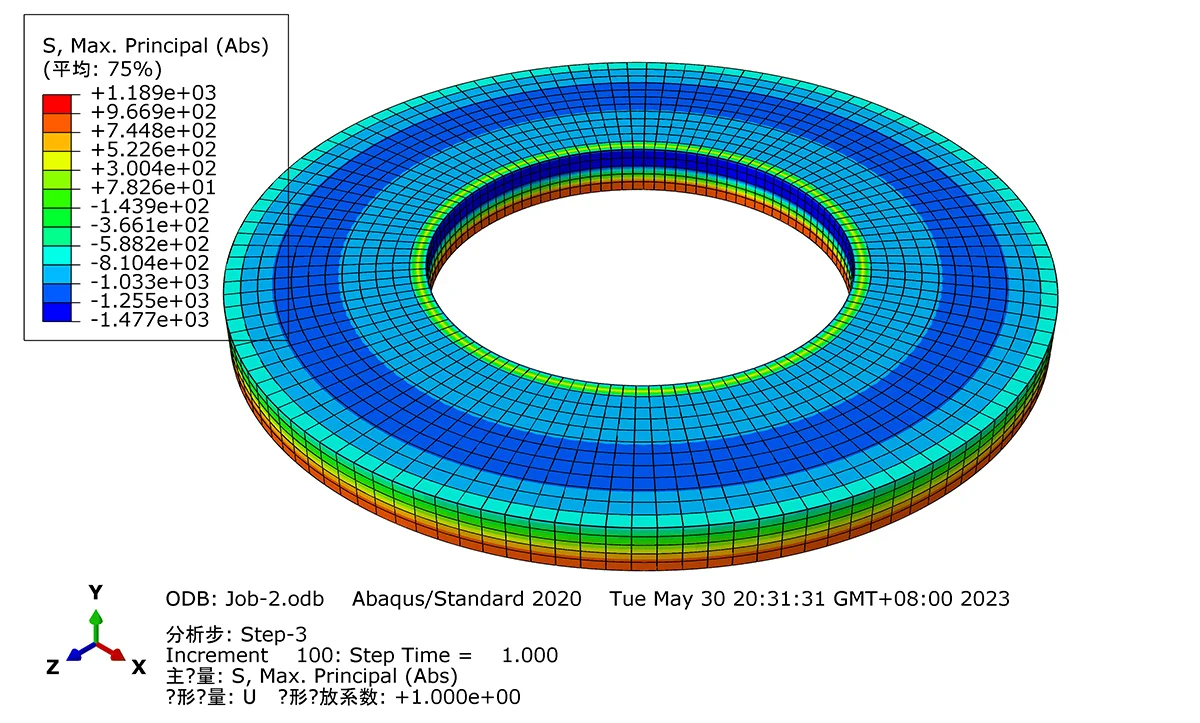
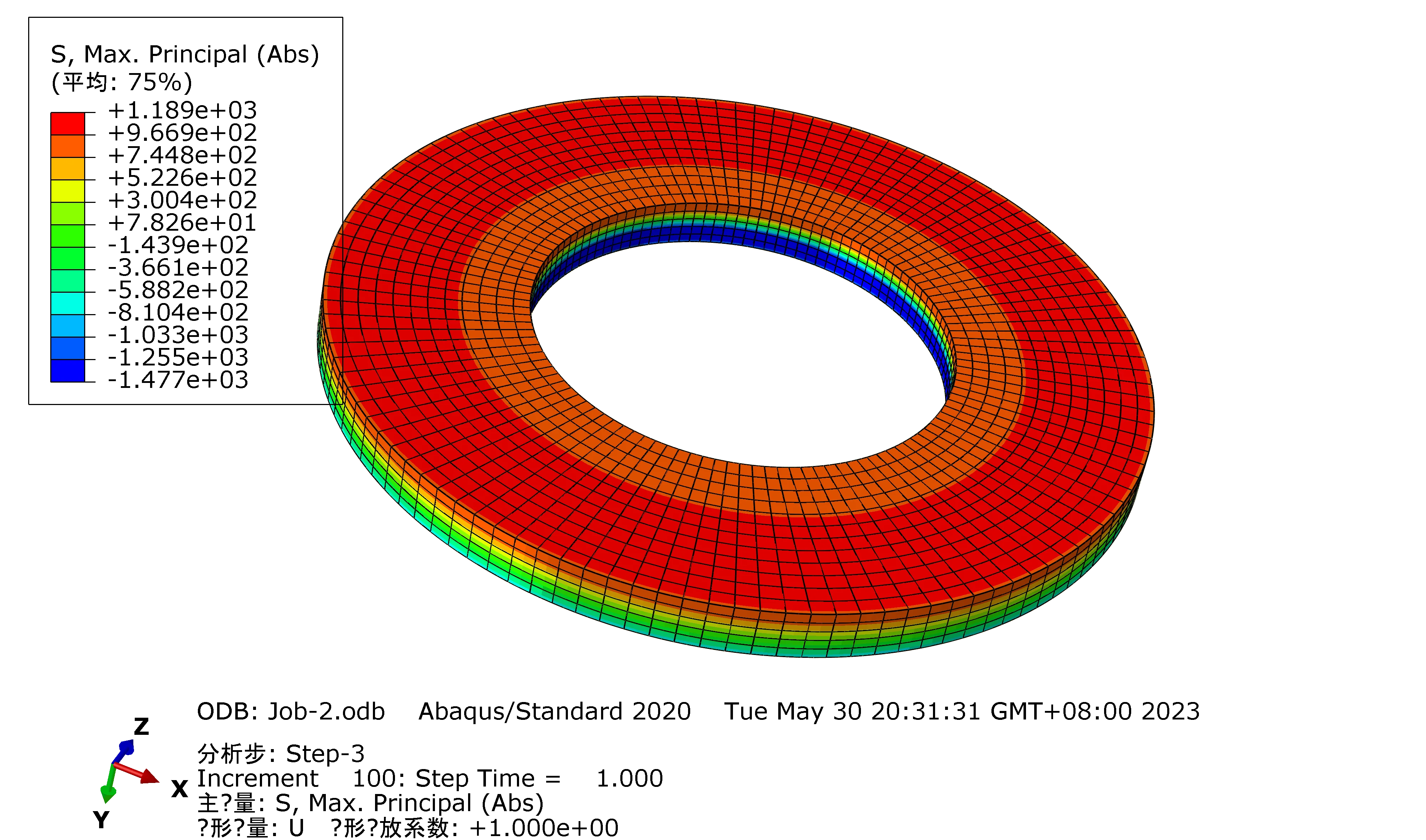
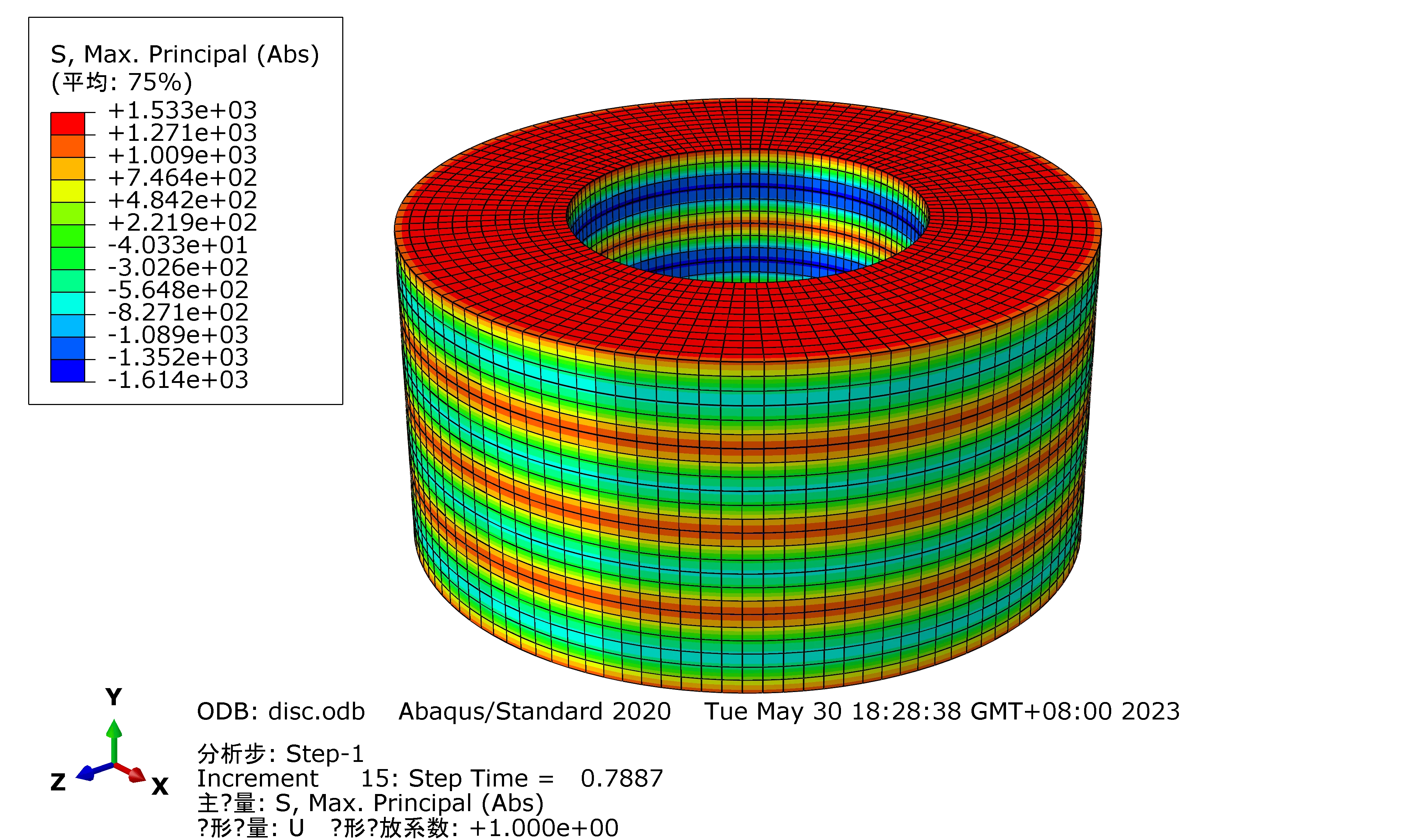

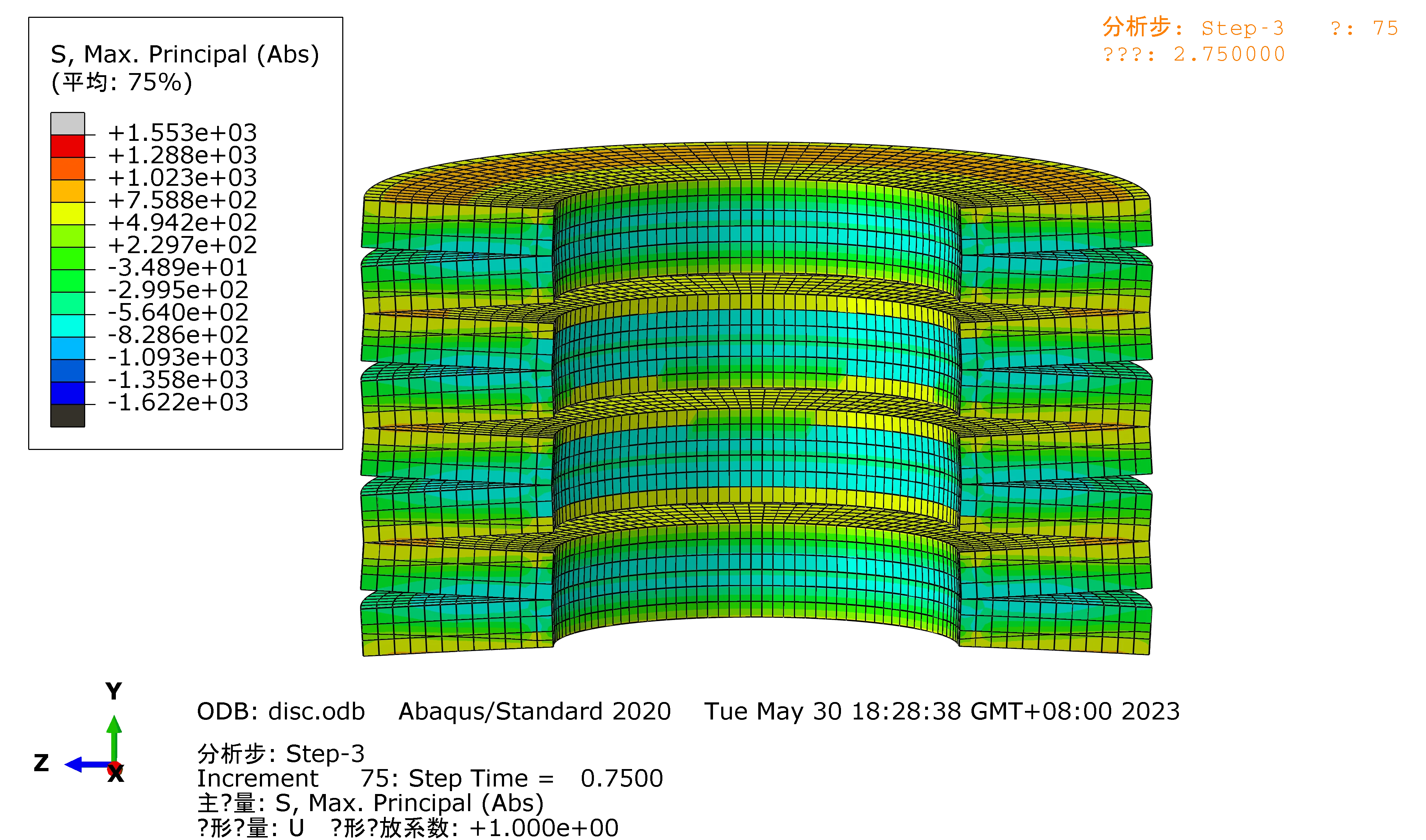
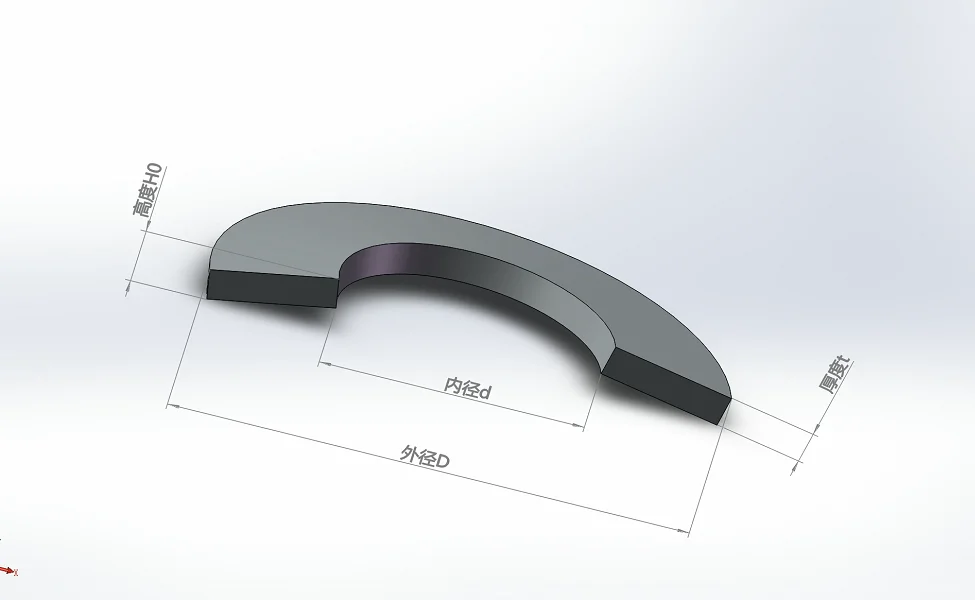
Raleigh Spring can also customize according to your special requirement.
Whether you're eager to learn, cooperate, or just have a friendly chat...
Whether you'd like... we'd love to hear from you.
Let's embark on an exciting journey together!